Lichen Planus
Author: Dr Haya Alani
Chief Editor: Dr Daniel Keith
Lichen Planus (LP) is an idiopathic, non-infectious inflammatory rash that can appear on different parts of your skin and mucous membranes including the inside of your mouth. It usually has a shiny, raised macroscopic appearance with a purple-red or white colour and can be itchy or sore if in the mouth.
Macroscopic Appearance

Macroscopic appearance in Fitzpatrick Skin Type 3
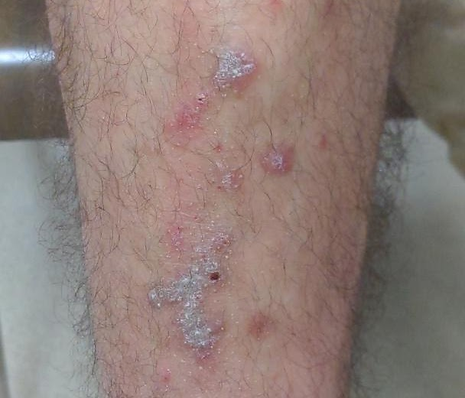
Macroscopic appearance in Fitzpatrick Skin Type 2

Macroscopic appearance in Fitzpatrick Skin Type 2

Macroscopic appearance in Fitzpatrick Skin Type 3

Macroscopic appearance of violaceous scaly papules in Fitzpatrick Skin Type 5 with significant post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation

Macroscopic appearance of Wickhams’s striae in the mouth in Fitzpatrick Skin Type 5

Macroscopic appearance in Fitzpatrick Skin Type 2

Macroscopic appearance in Fitzpatrick Skin Type 3
Dermoscopic Appearance
Wickham Striae are white crossing streaks corresponding to the focal thickening of the granular layer on histology and is known as the hallmark sign of Lichen Planus. It is the diagnostic key to differentiate between Lichen Planus and similar looking entities such as Psoriasis and Pityriasis Rosea. They are usually seen in the active phase of the disease and disappear after treatment thus their presence can be considered as an activation marker of Lichen Planus.
Different patterns of Wickham Striae exist including reticular (most common), circular, radial linear, globular, leaf-venation (fern-leaf) and clustered/ follicular (starry-sky) forms.

Example 1 (unannotated)
Under inflammoscopy in this example of a Fitzpatrick Type 3 patient, the simplest appearances include:
-
White, pearly broad reticulated Wickham Striae mainly at the periphery of the lesion
-
White and yellow dots surrounded by radial and linear red dotted vessels
-
Peripheral striations
-
Globular Wickham Striae

Example 1 (annotated)
-
White broad reticulated Wickham Striae (green)
-
White and yellow dots surrounded by red dotted vessels (yellow arrows)
-
Globular Wickham Striae (orange circle)

Example 2 (unannotated)
Under inflammoscopy in this example in the same patient with Fitzpatrick Type 3 skin, the features include:
-
White and yellow dots surrounded by radial and linear red dotted vessels
-
Peripheral striations

Example 3 (unannotated)
This example shows:
-
White and yellow dots surrounded by red dotted vessels

Example 4 (unannotated)
In this example in you can see:
-
Reticular and circular
-
Wickham Striae with radial streaming on a pink/red background

Example 2 (annotated)
-
Peripheral striations (red arrows)
-
White and yellow dots surrounded by red dotted vessels (yellow arrows)

Example 3 (annotated)
White and yellow dots surrounded by red dotted vessels (yellow arrows)

Example 4 (annotated)
-
Reticular and circular
-
Wickham Striae with radial streaming (green)
-
Pink/red background (orange)
Example 5 (unannotated)
In this example on Fitzpatrick Type 3 skin, but different lesion you can see:
-
Lacy white Wickham Striae with yellow perifollicular comedo like openings characteristic of Hypertrophic Lichen Planus.

Example 5 (annotated)
-
Lacy white Wickham Striae (green) with yellow perifollicular comedo like openings (yellow circles) characteristic of Hypertrophic Lichen Planus.

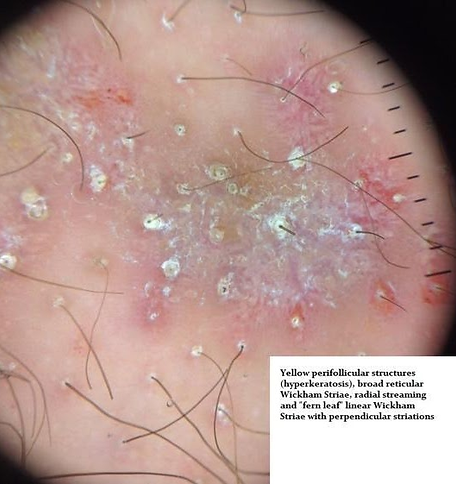
Example 6 (unannotated)In this example on Fitzpatrick Type 3 skin, but different lesion you can see:
-
Yellow perifollicular structures (hyperkeratosis) and comedo like openings
-
Broad reticular Wickham Striae with radial streaming and ‘fern leaf’ patterns

Example 6 (annotated)
-
Yellow perifollicular structures (hyperkeratosis) and comedo like openings (yellow circles)
-
Broad reticular Wickham Striae with radial streaming and ‘fern leaf’ patterns (yellow)

Example 7 (unannotated)
Under inflammoscopy in this example of a Fitzpatrick Type 5 Lichen Planus patient you can see:
-
Central pink/ violaceous lesion
-
Peppered pigmentation around the periphery of the lesion
-
Wickham Striae in a radial streaming (green) and circular pattern (orange)

Example 7 (annotated)
-
Central pink/ violaceous lesionPeppered pigmentation around the periphery of the lesion (similar to animated image in right bottom corner)
-
Wickham Striae in a radial streaming (green) and circular pattern (orange)
Note: peppering pattern is seen in the early phase of disease which then progresses to the reticular pattern over time.

Example 8 (unannotated)
In the same patient with Fitzpatrick Skin Type 5, but a different lesion you can see:
-
Wickham Striae with arboriform perpendicular ‘fern leaf’ projections
-
Yellow and white dots and globules with pigmented background and absence of Wickham Striae
-
Diffuse and perifolicular peppery pigmentation


Example 8 (annotated)
-
Wickham Striae with arboriform perpendicular ‘fern leaf’ projections (red)
-
Yellow and white dots and globules (blue) with pigmented background and absence of Wickham Striae
-
Diffuse and perifollicular peppery pigmentation (green)

Example 9 (annotated right, unannotated above)
-
Linear Wickham Striae (red) with brown dots and globules (purple)
-
White and yellow dots and globules (yellow)
-
General hyperkeratosis (scale)


Example 10
This further macroscopic example of LP presented as an itchy isolated plaque on the face of a young woman with Fitzpatrick type 6 skin.
Images credited to Mr Christopher Wearn, Consultant Plastic Surgeon.

Dermoscopic view of the same lesion as above (unannotated).

Dermoscopic view of the same lesion as above (annotated).
The features on dermoscopy shown in this annotated example:
In addition to the Wickham's striae (yellow arrows) and accentuated follicular openings (green circles), there is peripheral pigment loss where you see lightening at the edges before transition to normal skin (red arrow). This is supposed to be an indicator of inflammation in the skin and reduced melanin production.
If you'd like to extend your knowledge on this topic, read about Annular Atrophic Lichen Planus which is a rare variant of Lichen Planus.
